All tax returns we did in these courses are individual income tax returns. The official name is “T1 General Income Tax and Benefit Return”. Every adult Canadian resident should file individual income tax return every year.
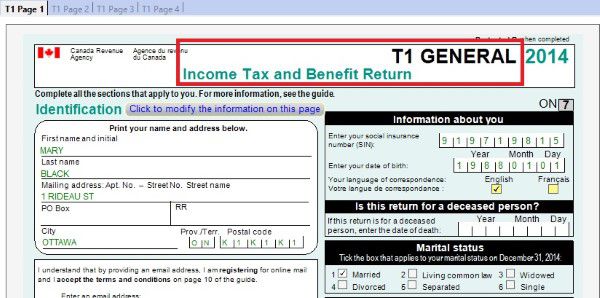
Individual income tax return has four main pages.
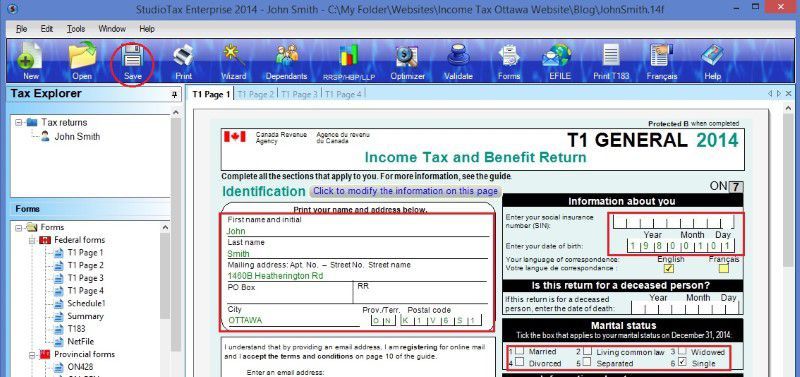
- T1 Page 1 includes your personal information.
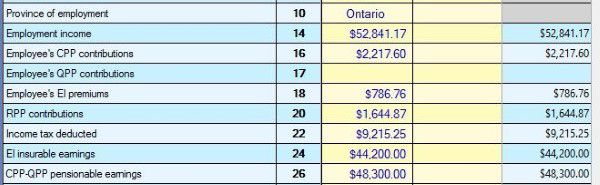
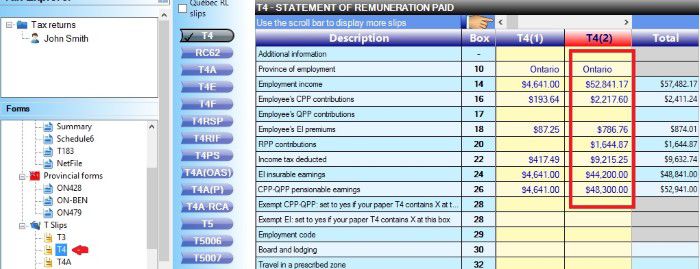
- T1 Page 2 contains your incomes such as employment income, self-employment income, and rental income.
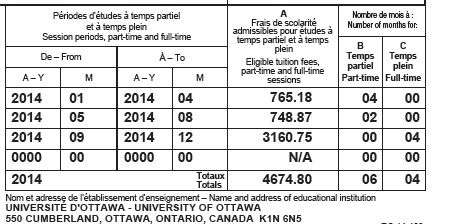
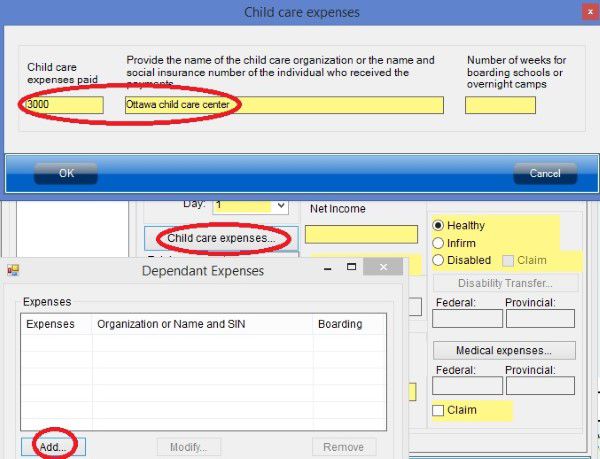
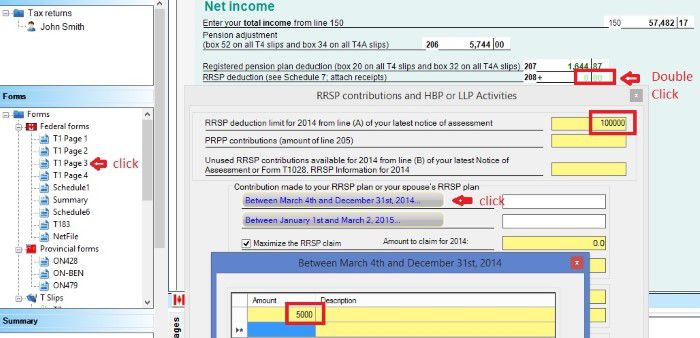
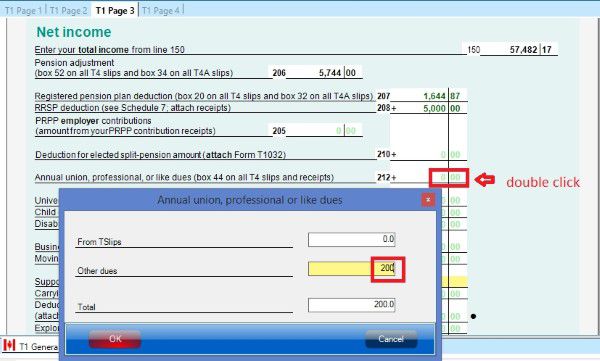
- T1 Page 3 has all your tax deductions such as RRSP deduction, child care expenses deduction and employment expenses deduction. For more information about tax deduction, read Tax courses 4: Understand tax deduction.
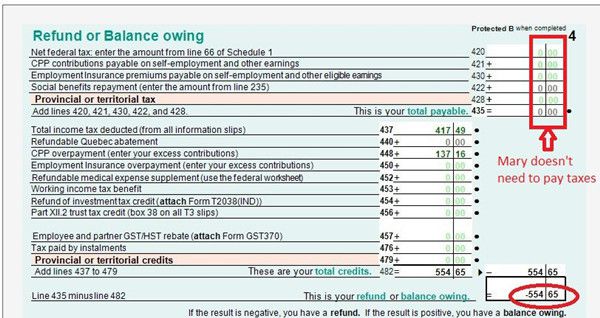
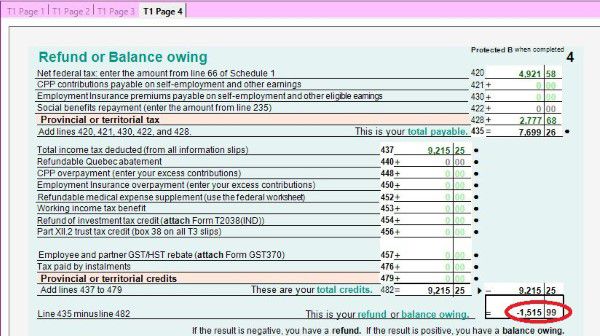
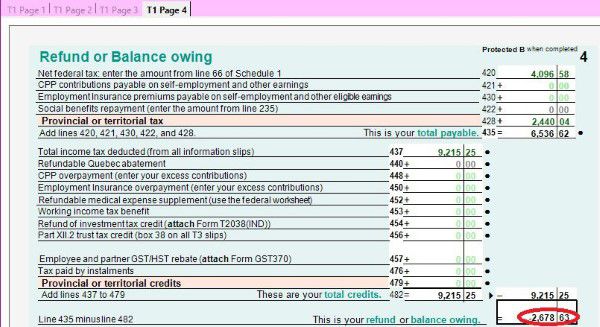
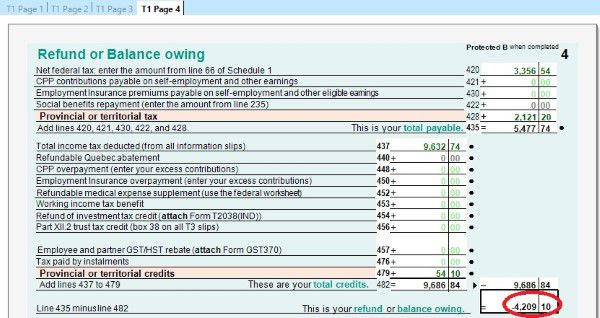
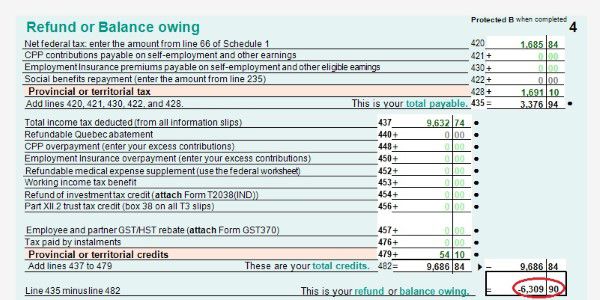
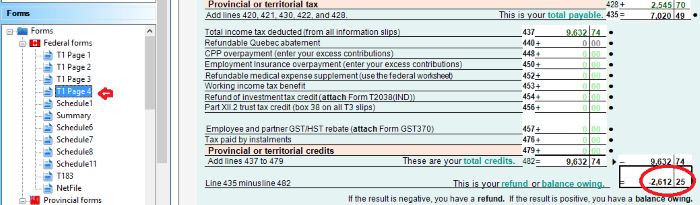
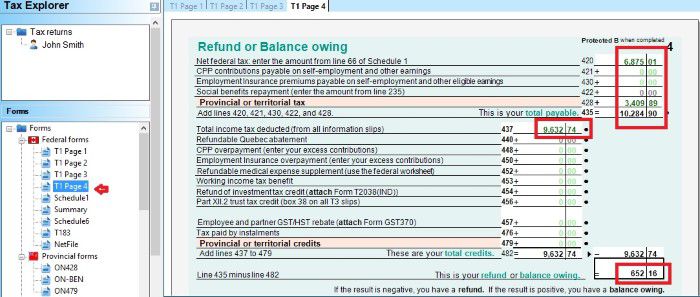
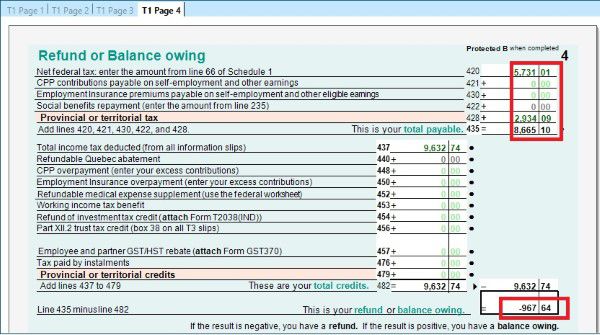
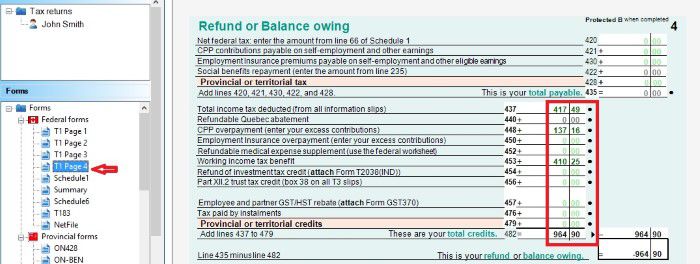
- T1 Page 4 shows the result – How much you owe or get refund. You can also enrol for direct deposit by input your bank account. If you have to mail your tax return, you have to sign on this page too.
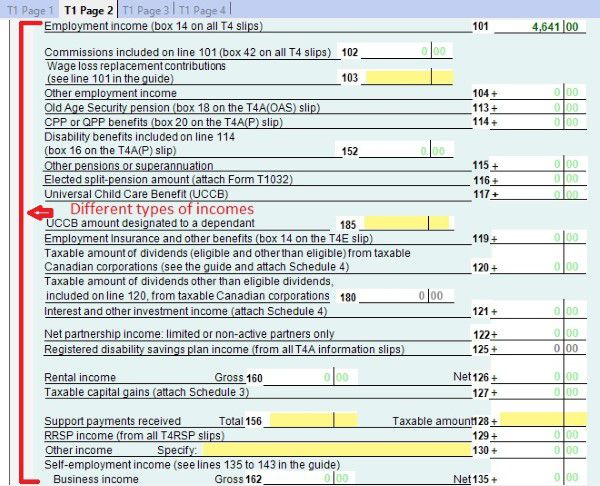
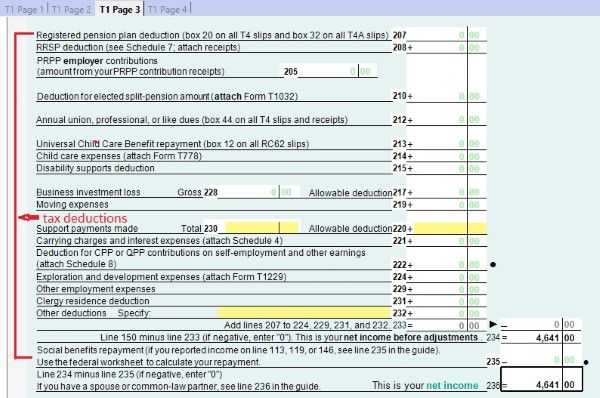
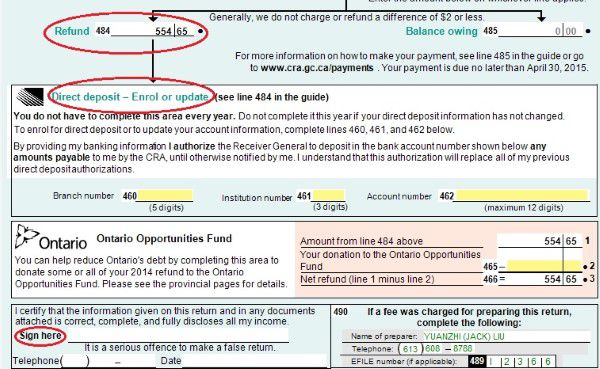
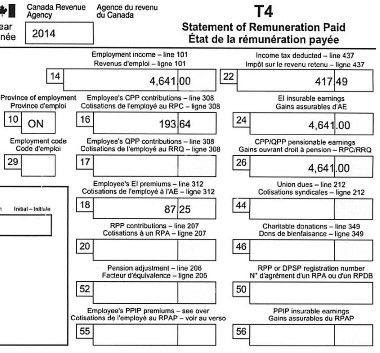
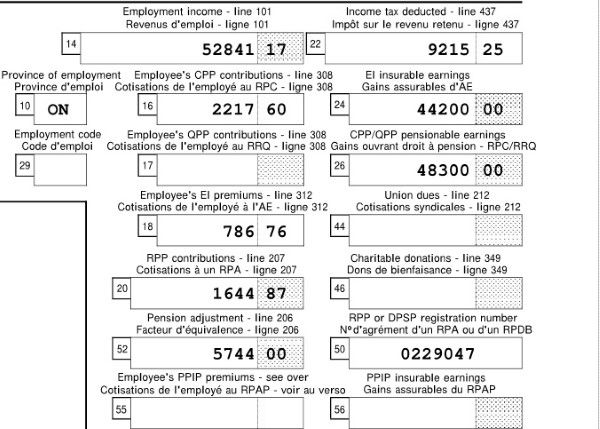
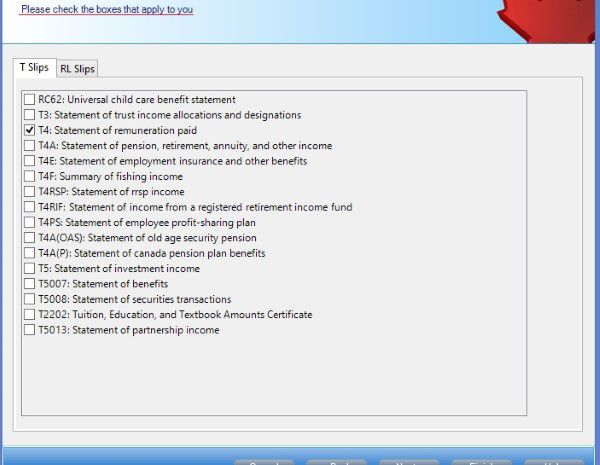
Every time you need to check or change something, you can do that by going directly to the according page. For example, if you want to claim your universal child care benefit, you can go directly to page 2 and double click line 117, and input the number into the pop-up form RC62.
Important schedules on your individual income tax return
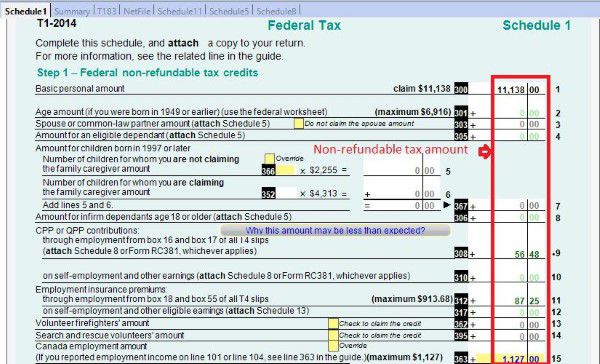
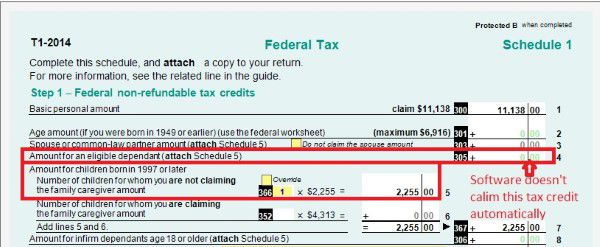
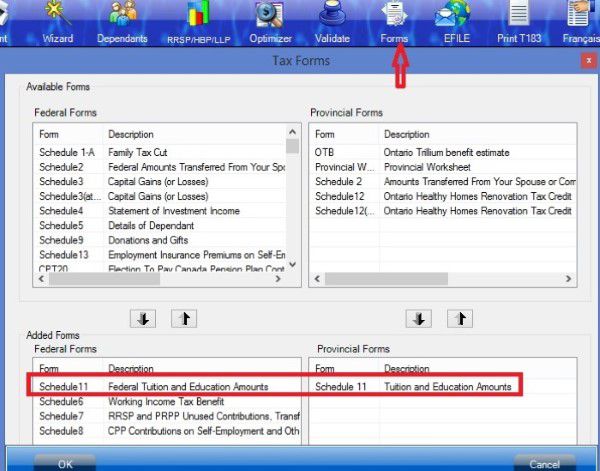
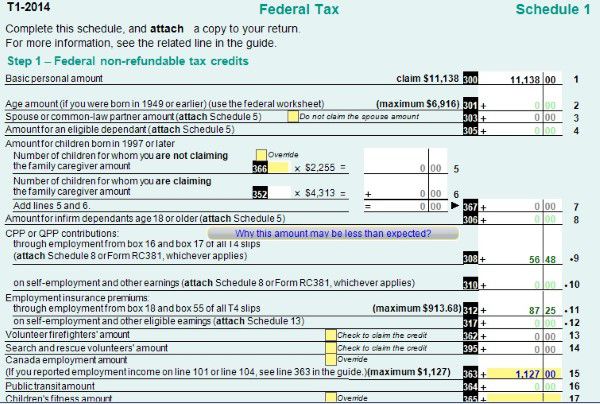
Schedule 1 must be included on your individual income tax return.
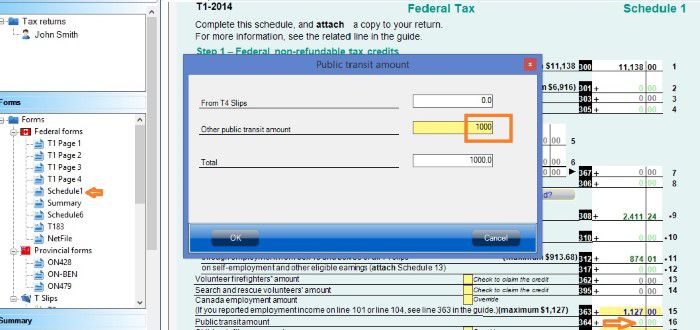
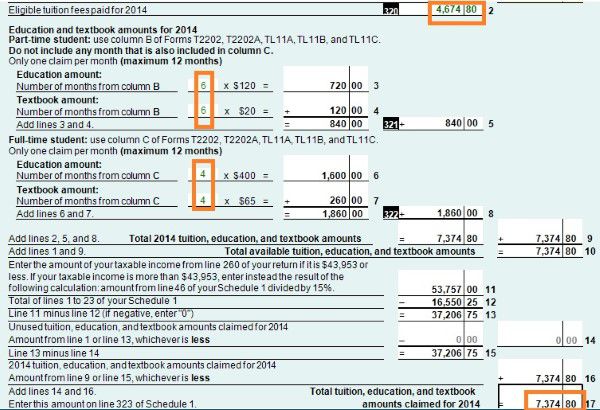
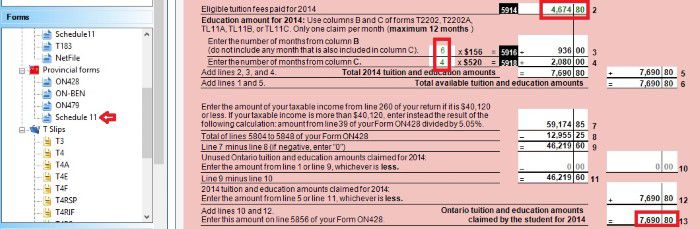
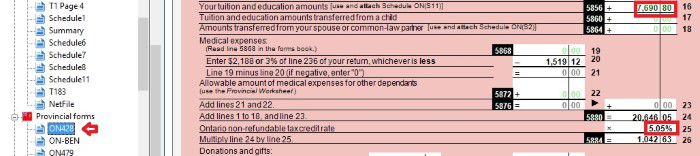
On schedule 1, you claim your Federal non-refundable tax credits such as public transmit amount, tuition amount and basic personal amount. Read more on Tax course 5: Understand tax credit.
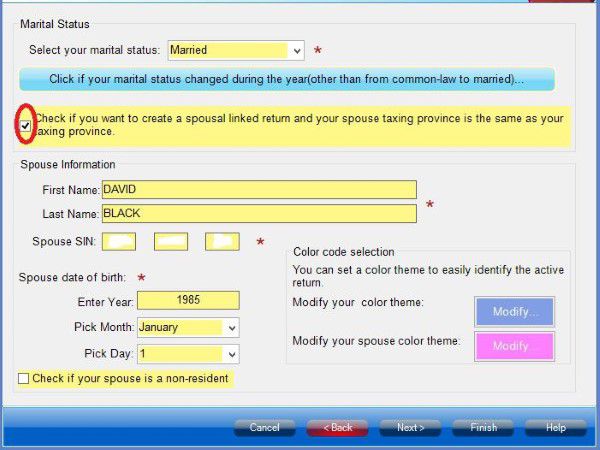
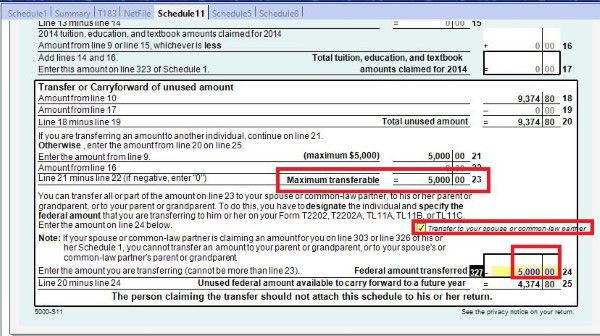
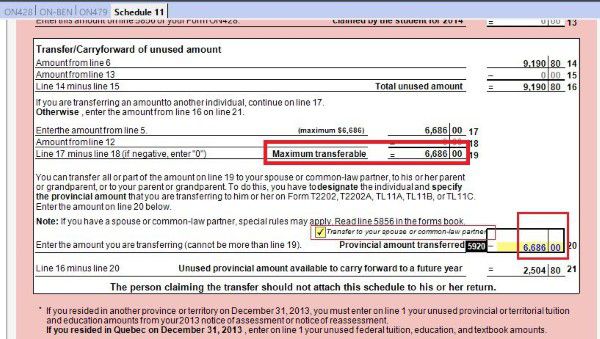
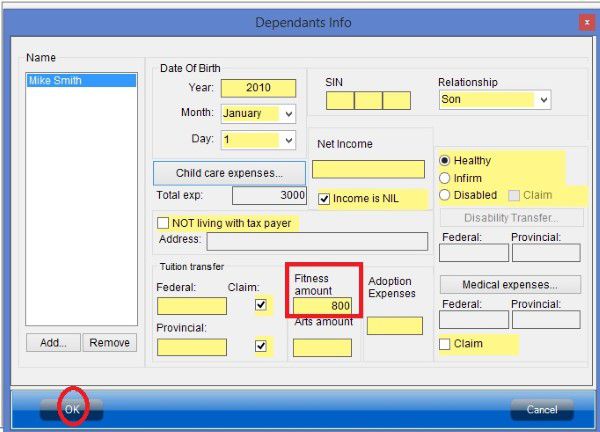
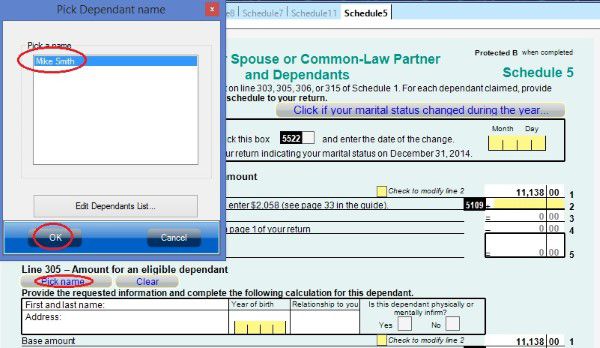
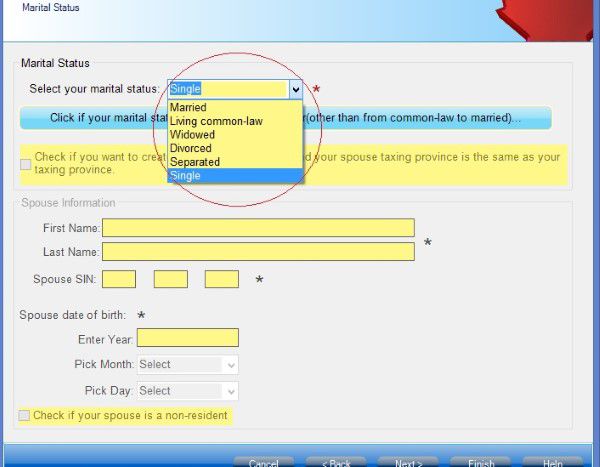
Schedule 5 where you claim amount for spouse or common-law partner and dependants.
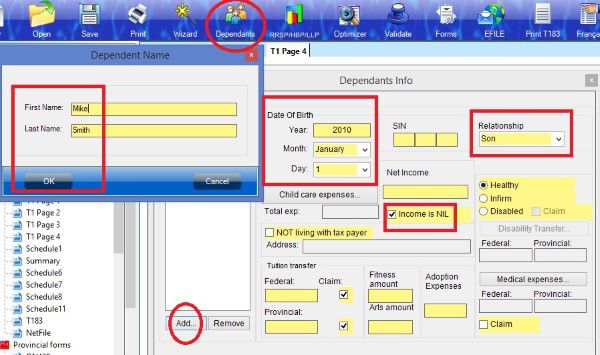
If you are single parent, don’t forget claim your child as eligible dependant in schedule 5. If you are married or live common-law and your partner is low income, you may be able to claim spouse or common-law partner amount.
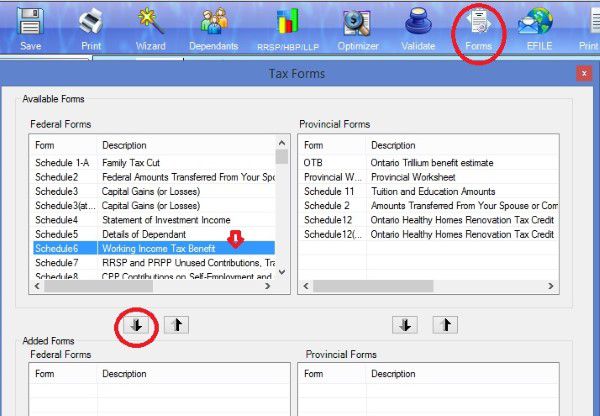
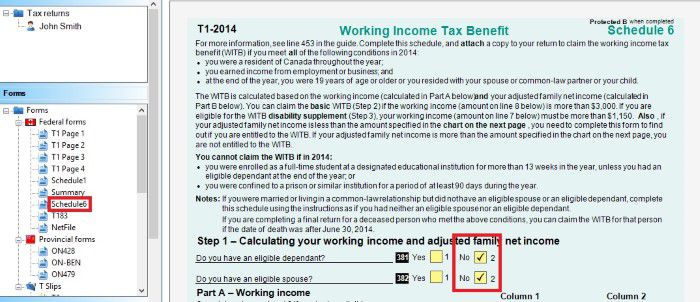
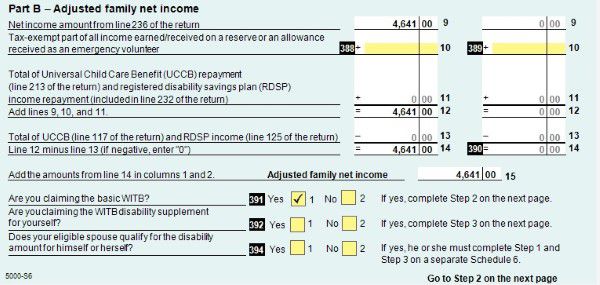
Schedule 6 to claim working income tax benefit
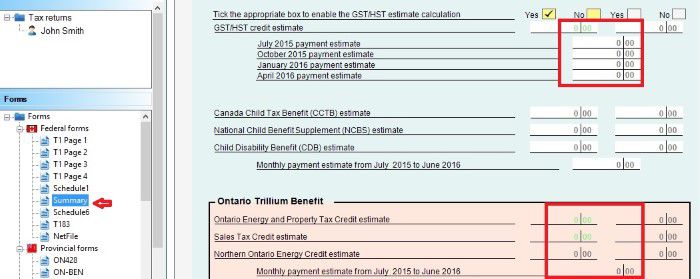
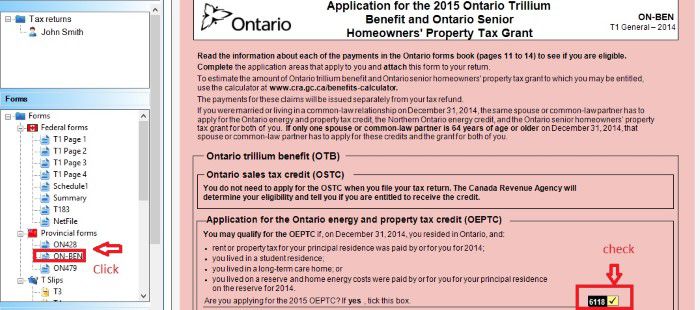
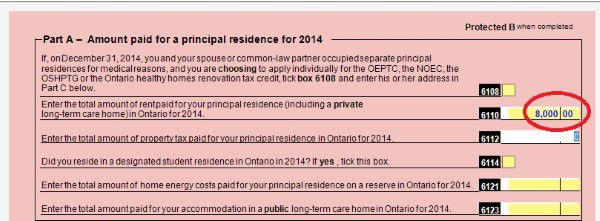
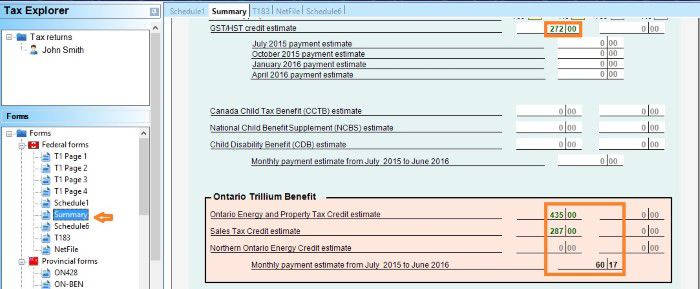
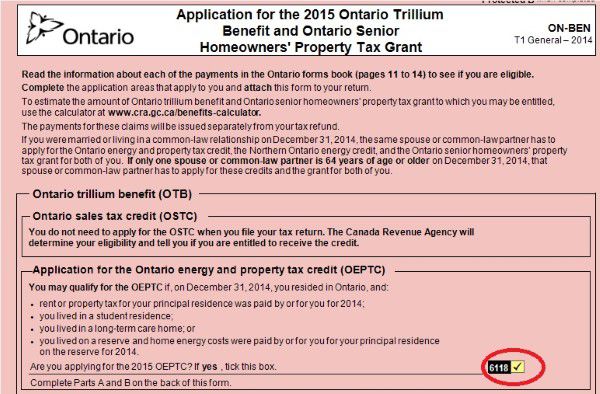
Ontario tax form ON-Ben to claim your rent or property tax payment.
Check the box.
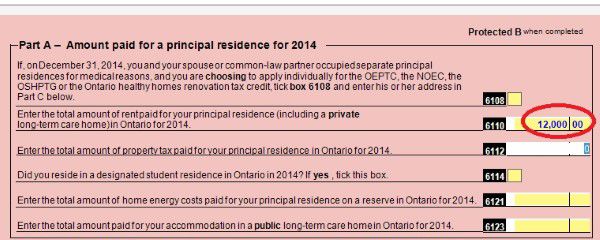
Input your rental payment amount.
The more you practice, the more you will understand your individual income tax return.Click to read all articles about Tax Courses.